Breaking RSA Encryption on Hardware Devices with Side Channel Power Analysis — Leaking the Private Key by Exploiting Square-Multiply Algorithm
Preface: This article is about leaking the private key from hardware devices that implement RSA encryption which is part of hardware hacking. The author is not responsible for any damage caused by the given information. It is recommended to be careful while performing these attacks as they can damage the hardware or even destroy it. All the information provided here is for educational purposes. There are no such prerequisites for understanding the theory, although knowledge about modular arithmetic, basics of encryption mathematics, basic electronics, etc. is recommended to carry out these attacks practically. Rest of all, hacking is about learning and having fun, so enjoy the cool attacks!
Introduction to Side Channel Power Analysis — Constant Emission of Information by Hardware Devices
Side Channel Analysis refers to extracting information from mediums that have relations with the elements interacting with the information and their behavior is influenced by the information processing. For example, using an infrared camera for monitoring heat from devices and finding faults in them through the heat traces. Another example is using signal processing on data containing the vibrational traces from objects that were due to sound in the area of people talking (vibrations can be taken from soundproof rooms too, allowing listening of conversations from soundproofed rooms). In the context of electronic devices for power consumption, information about the internal state of the processor is determined by analyzing the power consumption of these devices.
While microprocessors process information and execute instructions, they consume different amounts of power, if analyzed carefully. Since the voltage largely remains constant, the current consumption varies as per the required power by the processor. For example, adding instructions consumes relatively less power than the multiple instruction. Hence, the power consumption of the processor is analyzed to derive which instructions have been executed in the processor. This opens a lot of possibilities for leaking information from the processors, which in the case of cryptographic information which largely relies on computations and algorithms for optimization, has a lot of potential surface for hackers.
Introduction to RSA Encryption — Rivest-Shamir-Adleman Encryption
The RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a public-key cryptosystem that encrypts and decrypts data with the help of private and public keys. It’s a popular and secure algorithm that’s used for many applications, including digital signatures.
This cryptosystem is widely used for encrypting and decrypting data for secure transmission of data and has a huge number of applications. In this article, the mathematics of this algorithm will be explained in the next section since it’s important to understand the mathematics behind it and optimizations that have been made for computing this faster on processors with memory efficiency. Here, the explanation would be in a simple way, essential for side-channel analysis. For in-depth knowledge about this algorithm, refer to the Wikipedia page which has extensive documentation on this algorithm.
Wikipedia link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA_(cryptosystem)
Understanding the RSA Algorithm — Generating Keys and Encryption/Decryption
To understand the mathematics of the RSA algorithm, there are a few prerequisites of concepts that will be explained here. Feel free to jump to the mathematics if you are already familiar with them.
The factor of a Number
A number can be broken down into multiples of different numbers. For example, 20 = 2 * 2 * 5 or 20 = 1 * 20 which makes 1, 2, 5, and 20 the factors of the number 20. Every number is divisible by 1 and itself.
Prime Numbers
Numbers that have only two factors, that is 1 and itself if termed as a prime number. These numbers are not divisible by any number other than 1 and itself. Except for the number 2 which is prime and even, all other prime numbers are odd. For example, 7 has factors 1 and 7.
Semi Prime Numbers
Numbers that have their factors as 1 and itself as well as only prime numbers are called semi prime numbers. For example, 15 has its factors 1, 3, 5, and 15 where 3 and 5 are prime numbers.
Modulo Function
As shown in the equation given below, k is the remainder when m is divided by n.

For example, 10.mod(6) = 4 since when 10 is divided by 6, the remainder is 4.
A practical example of the modulo function: This is a very famous example that explains the use of the modulo function. Analog clocks with arms usually are in a 12-hour format. To show the time 15:00 in this 12-hour format clock, the hour arm is on 3:00 as per the 12-hour format. The equation for the conversation can be written as:
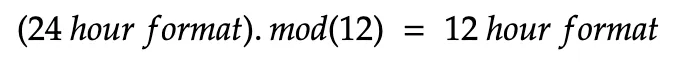
As shown in the equation, an example can be given for 15:00: 15.mod(12) = 3, which shows 3:00 in the 12-hour clock. Hence, the modulo function can be considered as a wrapping function, if imagined visually.
These were some of the concepts that are required to understand the RSA algorithm. Moving ahead, the RSA algorithm can be explained in two parts: Generating the Keys and Encryption/Decryption Mechanism.
The RSA Algorithm: Generating Keys
RSA Encryption includes pairs of two keys: Public Key and Private Key. To derive these keys, two numbers, p, and q are chosen. These are relatively large prime numbers that are difficult to guess. They are used to form n, which is a semi-prime number with factors p and q. With that, a totient t is calculated as shown in the equations given below.
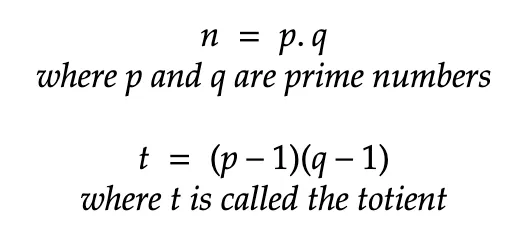
For generating Public Key E, 3 rules must be followed:
- E must be a prime number
- E must not be less than the totient
- E must not be the factor of totient

For generating Private Key D, a single rule needs to be followed:
The product of D and E, divided by T must result in a remainder of 1.

By generating the Public and Private Keys with given conditions and parameters, they can be used for encryption and decryption of data.
The RSA Algorithm: Encryption and Decryption
The encrypted plain text data is called the cipher text. Data can be encrypted by the public key, in which case the private key is used to decrypt the data whereas if the private key is used to encrypt the data, the public key is used to decrypt the data.
Following are the equations for encrypting and decrypting messages with Public and Private Keys.

These operations can be performed to implement RSA Algorithms for encryption of data during transmission. Without the Public Key/Private Key, the messages cannot be encrypted/decrypted.
This was the mathematics for the RSA Algorithm explained in a simple way and as required to understand the exploitation.
Identifying the Attack Surface of the Algorithm — Exploiting Optimisations for Efficient Computing
The Public Key E and the Private Key D are very big prime numbers that are mathematically infeasible to derive. Since they are so large numbers, exponentiation also takes a large amount of time. Hence, to optimize the exponentiation process, a method is used called the square-and-multiply algorithm. The final goal is to reduce the computational efforts to find the exponent by breaking the number into parts and reaching the goal with as few operations as possible.
It is essential to understand this algorithm since this is the attack surface that is going to be exploited with side-channel analysis.
To break the number into components, convert the exponent into its binary number format. The idea is to build up the number from its unity exponent i.e. to build up x to the power m from x to the power 1 where 1 is in binary.
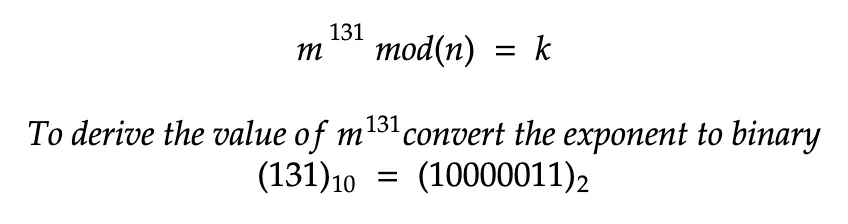
For example, consider the number 131 which is a prime number and has been converted to its binary form.
To find the exponents of the given number, two operations should be followed, and build up the number which is required for exponentiation.
- To append 0, square the number with the current exponent.
- To append 1, first square the number and multiply it by itself.
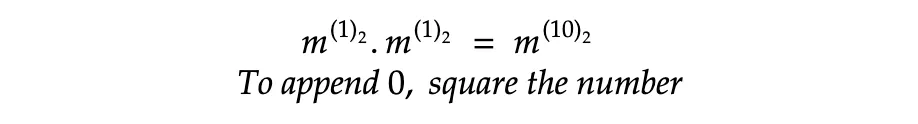
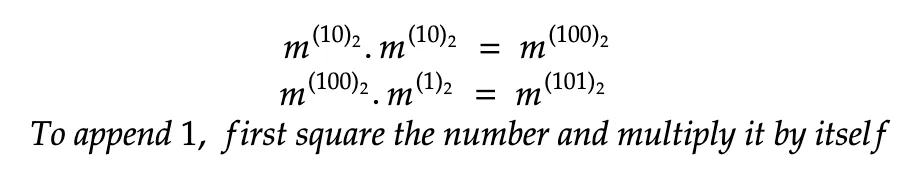
With these operations in line, the exponent can be constructed and when converted to the decimal form, it’s the private key as the exponent.
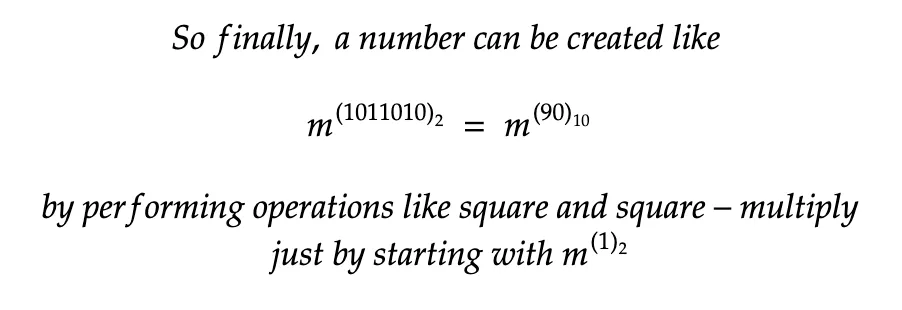
The processor performs square and multiply operations to find the exponent of the number m (which is the data to be decrypted).
Attacking the Square-Multiply Algorithm with Side Channel Power Analysis
Side Channel Power Analysis Attack
Now since the multiply and square operations take different amounts of computational effort, the processor consumes different amounts of power to computer it. Since P = VI where V is the potential difference across the component and I is the current flowing into the component, these parameters can be varied and the equation remains true. The voltage across the processor remains constant by design, but the current is allowed to vary when the power consumption changes.
Hence, the change in power consumption can be calculated by calculating the current flowing into the component. Hence, traces of power consumption can be taken to find out the operations that are happening inside the processor. This is called a Side Channel Power Analysis Attack, where power is used as a medium to derive information from a certain device.
Calculating the Power Consumption of the Processor
To calculate the current flowing into the component, oscilloscopes can be used. Since oscilloscopes can only measure voltage (usually), a shunt resistance can be used to find the value of current by the application of Ohm’s law.
Ohm’s law states that the electric current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the three mathematical equations used to describe this relationship:
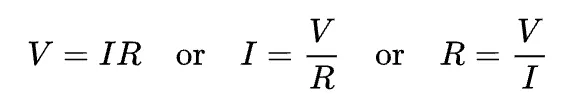
By calculating the voltage across the shunt resistance, variations in the current values can be determined, which in turn can be used to determine the power variations and finally, the operations that are executed in the processor.
It is recommended to remove the capacitors that influence the power consumption since they interfere with the readings by discharging while power goes down and charging while power goes up, to improve the quality of data.
Deriving the Private Key by the Analysis of Power consumption
From the example shown above, these computations are done to derive the exponent, which is the private key. A combination of squares and multiplication is done here to derive it.
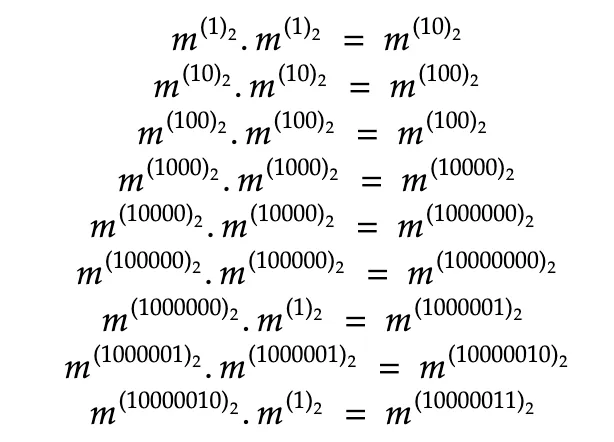
Following is the sequence of operations performed on the numbers.

When there is a square operation, a 0 is appended to the formation of the private key. Hence, a square operation indicates a 0. Note that the first digit (the most significant bit would be 1 as the computation begins with the number itself). When there is a square followed by multiply, the digital 1 is appended, indicating 1.
Hence, by the sequence of operations done about, 100000101 can be derived which is the private key.
This sequence of operations can be derived from the power traces of the processor. Since the multiplication operation consumes relatively less power than the square operations, these fluctuations can be analyzed to derive the sequence of operations in the processor to derive the private key of the RSA implementations.
Conclusion — Acknowledging the Information Leaks by Hardware Devices
Side Channel Analysis in the context of power analysis can reveal a lot of information and even leak the private key from the processors and has a lot of potential for research in hardware-related attacks. RSA has a huge amount of applications and hardware attacks like these can have a lot of possibilities.